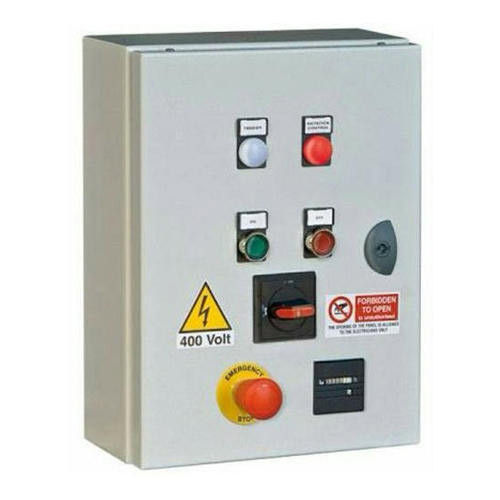
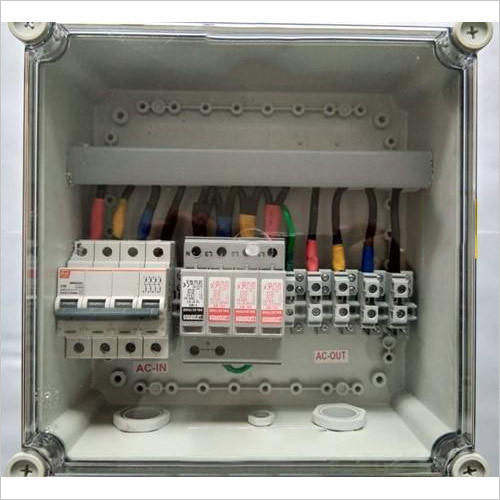
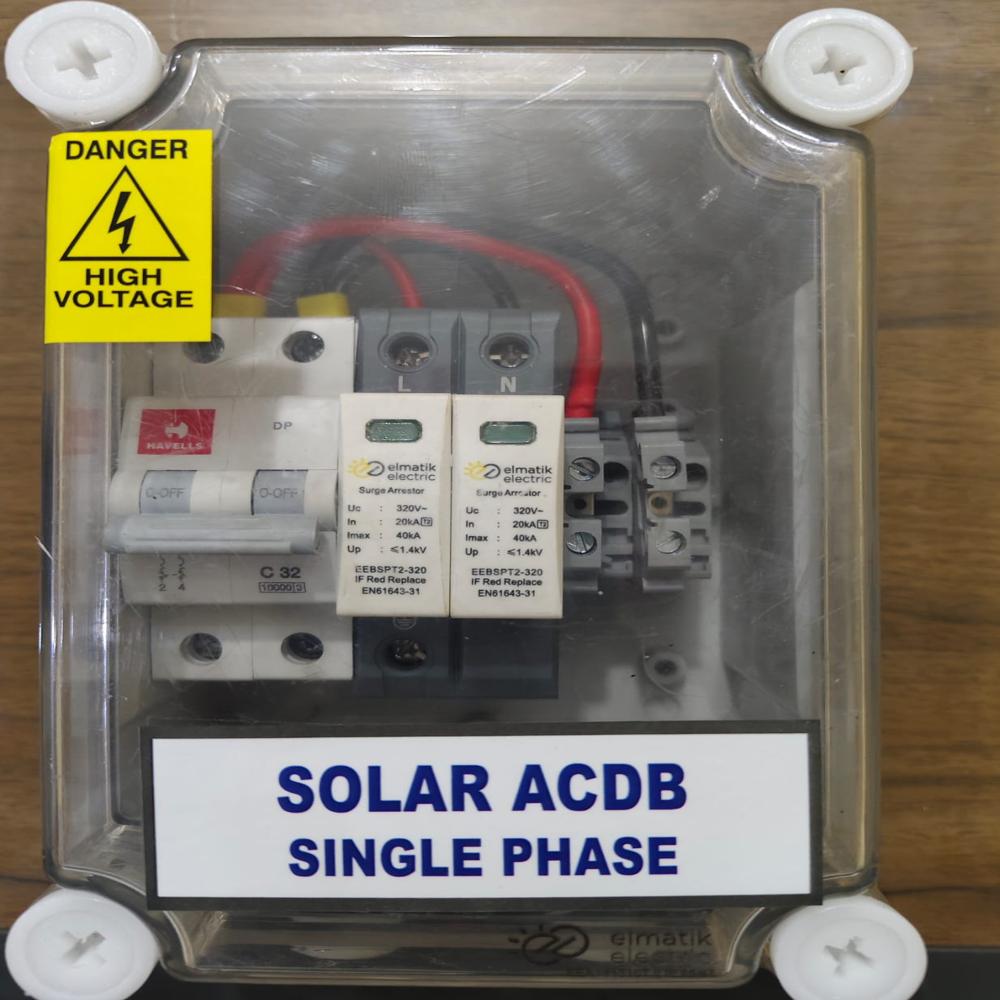
A Solar ACDB, or Solar Array Combiner and Distribution Board (ACDB), is a crucial component in any grid-tied or hybrid solar power system. It acts as an intermediary between the solar inverter(s) and the main AC distribution board of the building or grid.
Here's a detailed description:
Purpose and Function:
The primary purpose of a Solar ACDB is to:
- Combine AC Outputs: In systems with multiple string inverters, the ACDB collects the AC output from each individual inverter and combines them into a single, higher-capacity AC output.
- Protection: It provides essential electrical protection for the solar PV system, the inverter(s), and the building's electrical infrastructure. This protection includes:
- Overcurrent Protection: Using Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) or Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) to protect against overloads and short circuits.
- Surge Protection: Incorporating Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) to safeguard against lightning strikes and other transient voltage surges coming from the AC side.
- Isolation: Providing means of disconnecting the solar PV system from the main AC supply for maintenance, repairs, or emergencies.
- Metering and Monitoring (Optional but Common): Many ACDBs include provisions for metering the generated AC power. This can range from basic analog meters to advanced digital energy meters that communicate with monitoring systems.
- Distribution: It facilitates the safe and organized distribution of the solar-generated AC power to the load or to the grid.
Key Components within a Solar ACDB:
- Enclosure: A robust, weather-resistant (typically IP65 or higher for outdoor installations) enclosure made of metal (like powder-coated sheet steel) or high-grade plastic.
- Input Terminals: Connections for the AC output cables from each solar inverter.
- Output Terminals: Connection for the main AC cable going to the building's main distribution board or grid connection point.
- AC Circuit Breakers (MCBs/MCCBs): Sized appropriately for the inverter output currents and the overall system capacity. There will typically be individual breakers for each inverter input and a main output breaker.
- Surge Protection Devices (SPDs): Class II (Type 2) or Class I+II (Type 1+2) SPDs are commonly used on the AC side to protect against voltage surges.
- Busbars: Copper or aluminum busbars are used to combine the AC inputs from multiple inverters and distribute power.
- Wiring: High-quality, appropriately sized electrical wiring to handle the current.
- Indicating Lights (Optional): To show power status or fault conditions.
- Metering Devices (Optional): Energy meters (kWh meters) for measuring power generation.
Types and Configurations:
Solar ACDBs come in various configurations depending on the system size and number of inverters:
- Single Inverter ACDB: A simpler unit for systems with just one solar inverter.
- Multi-Inverter ACDB (Combiner ACDB): Designed to combine the outputs of multiple string inverters.
- ACDB with Metering: Includes integrated energy metering.
- ACDB with Communication: May have ports for communication with monitoring systems.
Importance:
The Solar ACDB is critical for:
- Safety: Protecting personnel and equipment from electrical hazards.
- System Longevity: Protecting inverters and other sensitive equipment from surges and faults.
- Compliance: Ensuring the solar installation meets electrical codes and standards.
- Efficient Operation: Providing a structured and reliable interface for the solar power generation.
In essence, a Solar ACDB is the brain and brawn of the AC side of a solar power system, ensuring safe, efficient, and protected integration of solar-generated electricity into the existing electrical infrastructure.